Fasting is a common cultural and religious practice followed by many people. However, fasting during pregnancy is generally not recommended, as this is a critical period where both the mother and the developing baby require continuous nourishment and hydration.
Why Fasting Is Not Recommended During Pregnancy
During pregnancy, your body undergoes significant changes and has increased nutritional demands. Skipping meals or avoiding fluids for long hours can negatively affect both maternal and fetal health.
Key reasons fasting is unsafe during pregnancy include:
Increased Nutritional Needs:
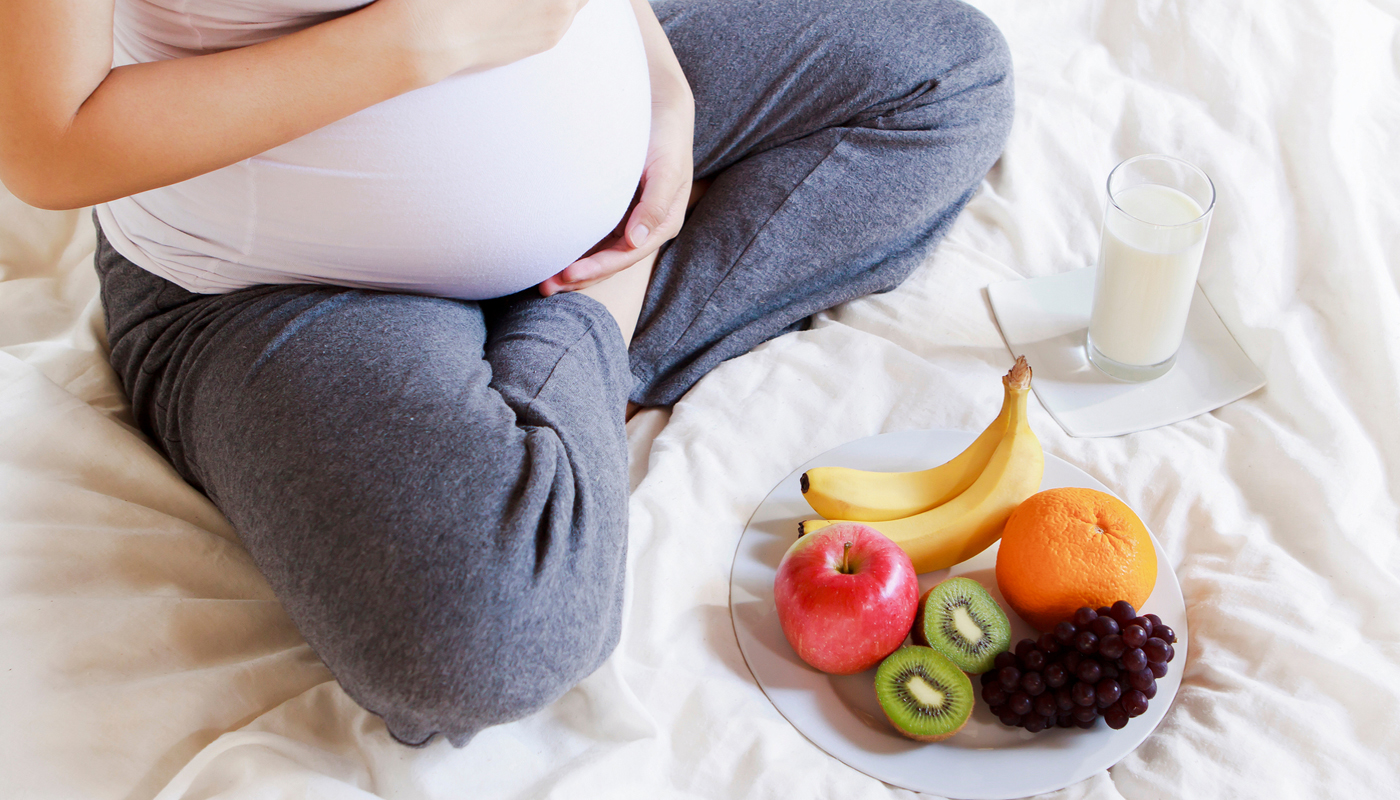
Pregnant women need adequate calories, proteins, vitamins, and minerals to support the babyĺs growth and brain development. Fasting may lead to nutritional deficiencies.
Risk of Dehydration:
Drinking enough water is essential during pregnancy. Fasting can cause dehydration, which may lead to dizziness, fatigue, low blood pressure, and reduced amniotic fluid levels.
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia):
Long gaps without food can cause blood sugar levels to drop, leading to weakness, headaches, fainting, and nausea.
Impact on Babyĺs Growth:
Prolonged fasting may reduce the supply of essential nutrients and oxygen to the fetus, potentially affecting fetal growth and development.
Increased Risk of Complications:
Fasting may increase the risk of preterm labor, urinary tract infections, and excessive fatigue, especially in women with anemia, gestational diabetes, or high-risk pregnancies.
Can Occasional or Short Fasts Be Considered?
In some cases, short fasting periods may be unavoidable due to religious or cultural reasons. However, this should only be done after consulting your obstetrician. Every pregnancy is different, and medical advice should be personalized based on your health, trimester, and pregnancy risk factors.
Doctors may advise:
Avoiding long fasting hours
Staying well-hydrated
Consuming nutrient-dense meals before and after fasting
Monitoring for warning signs such as dizziness, reduced fetal movements, or weakness
Healthy Alternatives to Fasting During Pregnancy
If fasting is part of a religious practice, consider safer alternatives such as:
Eating small, frequent meals
Avoiding dehydration by sipping water throughout the day
Choosing balanced meals with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, protein, and healthy fats
Following partial fasts with medical guidance
When to Seek Medical Advice Immediately
Stop fasting and consult your doctor if you experience:
Severe weakness or fainting
Persistent vomiting
Reduced fetal movements
Signs of dehydration
Abdominal pain or contractions
Final Thoughts
Pregnancy is a time when your health directly impacts your babyĺs well-being. Maintaining a healthy, balanced diet and proper hydration is far more important than observing fasting rituals during this period. Always prioritize medical advice and listen to your body.
If you are considering fasting during pregnancy, consult your gynecologist or obstetrician first to ensure the safety of both you and your baby.